Are you tired of dealing with frustrating internet connection issues and network connectivity problems on your Windows computer? Constantly struggling to establish stable network connections or experiencing slow internet speeds can be incredibly frustrating, especially when it is related to network information, such as cable modem and network adapters. But fear not, because help is here!
From common issues like limited connection or unidentified network errors to more complex performance troubles, we’ll cover additional troubleshooting steps for networks, including fixes for TCP issues. Whether you’re a tech-savvy individual or a beginner, this article will provide step-by-step guidance and helpful tips to troubleshoot common internet issues and get your internet connection through your wireless router up and running smoothly again. So, if you’re ready to take control of your network connection and bid farewell to those pesky issues with your Wi-Fi networks, Ethernet cables, and telnet fixes, keep reading!
Understanding Windows Network Connectivity Issues
Different Types of Network Connectivity Problems in Windows
Internet connection issues can be a common occurrence when using Windows, especially with networks. These problems can often be resolved by checking the ethernet cable. These network issues can manifest in various ways, such as slow internet speeds, intermittent connections, or complete loss of network access. If you are experiencing any of these problems, there are a few fixes you can try. First, check your wireless mode settings to ensure they are properly configured. Additionally, you can try pinging different networks to identify any potential issues. Understanding the various types of network connectivity problems, such as issues with networks and internet connections, is essential for effective troubleshooting. It is important to be familiar with commands like ipconfig when troubleshooting a new connection.
One type of issue with wireless networks is a “No Internet Access” problem, where the computer shows that it is connected to the network but cannot establish an internet connection. To troubleshoot this problem, you can use the ipconfig and telnet commands. This could be due to misconfigured internet connection settings or common connection problems with networks or issues with the DNS server.
Another common problem is when the computer fails to establish an internet connection with any wireless network due to connection problems. This may indicate a hardware issue like a faulty network adapter or incorrect driver installation, which can lead to common connection problems. It is important to check the device manager for any issues with your internet connection and networks.
Users may encounter “Limited Connectivity” errors with their internet connection, which commonly occur when the device connects to wireless networks but has limited access to resources or services. This could be caused by firewall restrictions or IP address conflicts, resulting in connection problems with network connections and the internet connection. It is also possible that there may be issues with network adapters.
Factors Contributing to Network Connection Failures
Several factors, such as issues with wireless networks or driver problems, can contribute to network connection failures on Windows systems. To troubleshoot these issues, you can use the ipconfig command to check the type of network connection and identify any potential problems. One major factor is incorrect configuration settings. Accurate configurations of IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS servers are crucial for proper network communication. If you experience connection problems, you can use the command “ipconfig” to check your internet connection.
Software conflicts, outdated drivers, and connection problems can also lead to network adapter connectivity issues. To resolve these problems, you can use the network adapter troubleshooter or network troubleshooter. Conflicting applications or outdated drivers may interfere with the functioning of network adapters and protocols, causing connection problems with the internet connection. It is important to regularly update your systems to avoid such issues.
Physical obstacles like distance from Wi-Fi routers or interference from other electronic devices can weaken or disrupt wireless signals, resulting in poor connectivity. If you are experiencing issues with your network connection, you can try performing a network reset or troubleshooting your network adapters using the network troubleshooter. Additionally, you can also check the network icon on your device for any error messages or notifications.
Moreover, malware infections can cause disruptions in network connections by modifying system files and configurations on your PC. These disruptions can be resolved by performing a timely update to your power source. Malware may also affect network adapters, causing issues that require the use of network troubleshooter and network commands. In some cases, a network reset may be necessary to resolve the problem. Additionally, malware can consume excessive bandwidth or redirect traffic through malicious proxies.
Impact of Network Issues on Overall System Performance
Network connectivity problems not only affect internet access but also impact overall system performance on Windows PCs. These issues can be resolved with a simple click by updating the network driver.
Slow internet speeds on a PC can be frustrating, as they can cause delays when you click on webpages and slow down downloads/uploads due to network issues. This can hinder productivity and frustrate users.
Network issues can also affect the performance of network-dependent applications and services on a PC. These issues can arise from problems with connecting to the network, outdated or incompatible drivers, or incorrect IP address configurations. For example, online gaming experiences on a PC may suffer from high latency or frequent disconnections due to issues with network adapters, making gameplay difficult or impossible. To resolve these issues, you can check your network profile settings or use the network troubleshooter to identify and fix any problems.
In addition to these direct impacts, network problems can indirectly affect PC performance by consuming excessive system resources. This can occur when the PC is unable to connect to a Wi-Fi network or when the driver for the network adapter is outdated or malfunctioning. When a computer struggles to establish a stable connection, it may continuously attempt to reconnect, leading to increased CPU and memory usage. This issue can often be resolved by utilizing network troubleshooter or resetting the network adapters. Additionally, checking the network icon can provide valuable information about the connection status. This can slow down other processes running on the pc, such as network adapters. To fix this issue, you can try performing a network reset or using network commands.
Initial Troubleshooting Steps for Network Problems
Basic Steps to Take When Encountering Network Connectivity Problems
When you encounter network connectivity problems on your Windows PC, it can be frustrating and disrupt your online activities. One common cause of these issues is an outdated driver for your network adapter. However, there are some basic steps you can take to troubleshoot and resolve these network issues with your PC. Use the network troubleshooter tool to check for any problems with your network adapters.
Firstly, check the physical connections and cables. Check that all network adapters are securely connected and not damaged. Sometimes, a loose or faulty cable can cause network problems when trying to connect your PC to a Wi-Fi network due to driver issues. If you are using an Ethernet cable for a wired connection, make sure it is properly connected to both your computer and the router or modem. Also, ensure that your network adapters are functioning correctly by checking their network adapter drivers. Additionally, double-check that you have entered the correct network name and that your network profile is properly configured.
Checking Physical Connections and Cables
To check the physical connections and cables:
- Check the network adapters on your computer and ensure the network adapter driver is up to date. Examine the Ethernet cable connecting your computer to the router or modem and perform a network reset if necessary. Ensure that it is firmly plugged into both devices.
- If you are using a wireless connection, check that your PC’s Wi-Fi adapter driver is turned on. If you encounter any issues, you may need to perform a network reset.
- If you suspect a faulty Ethernet cable, try using a different adapter or connect to a different Wi-Fi network if possible. Check the driver on your PC.
By checking the physical connections and cables of your PC, you can eliminate any potential issues caused by loose or damaged connections. Additionally, performing a network reset or updating the network adapter driver can help resolve connectivity problems.
Verifying Router and Modem Functionality
Another important step in troubleshooting network connectivity problems is to check the functionality of your PC, router, and modem. Verify the driver for your PC and ensure that the Wi-Fi is working properly.
- Check if other devices connected to the same network are experiencing similar issues with the PC adapter driver and Wi-Fi. If multiple devices cannot connect to the internet, there may be an issue with your router or modem. You can try performing a network reset on your PC or updating your network adapter driver. This can help resolve any connectivity issues with your Wi-Fi network.
- Restart your router and modem by unplugging them from power for about 30 seconds before plugging them back in to ensure a stable connection. This can help resolve issues with your network adapter driver and allow your PC to connect to the Wi-Fi network.
- Wait for a few minutes after restarting your pc to allow the router and modem to establish a stable connection. Make sure to check if your network adapter driver is up to date to ensure a smooth connection to the Wi-Fi network.
If these steps do not resolve the network problem on your PC, consider contacting your internet service provider (ISP) for further assistance or consult their support documentation.
Remember that these initial troubleshooting steps focus on checking physical connections, cables, and the functionality of your router or modem. Additionally, it is important to ensure that your PC has the appropriate network adapter driver installed for the type of Wi-Fi network you are trying to connect to. By ensuring that your pc’s network adapter driver is up to date, you can check for common connection problems caused by hardware issues on your fi network.
Using Windows Network Diagnostics Tools
The operating system provides several built-in tools to help identify and resolve pc network adapter driver connection issues. These pc tools are specifically designed to diagnose various aspects of network connectivity, such as IP configuration, DNS resolution, network adapter settings, and driver issues. When troubleshooting network problems, it is important to select the right type of tool for the job.
Overview of built-in network diagnostics tools in Windows
Windows offers a range of diagnostic tools that can assist in troubleshooting network connectivity issues on your PC. These tools can help identify and resolve problems with drivers and Wi-Fi connections. When facing network issues, you can select the appropriate diagnostic tool to diagnose and fix the problem. One such tool for troubleshooting network connectivity issues on a PC is the Network Troubleshooter. It can be accessed through the Control Panel or by right-clicking on the network icon in the system tray. The troubleshooter automatically scans the PC for common problems with the network adapter driver and offers suggestions for resolving them.
Another useful tool for troubleshooting network connectivity is ipconfig, a command-line utility that displays detailed information about IP configuration on your computer, including network adapter types and drivers. By typing “ipconfig” in the Command Prompt window, you can view details such as your IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server addresses, and network adapter driver.
Step-by-step guide on how to use the Network Troubleshooter
To use the Network Troubleshooter:
- Open the Control Panel on your PC by searching for it in the Start menu. This is where you can find and manage various drivers, including network adapters, to ensure a smooth and stable connection.
- In the Control Panel window, select “Network and Internet” and then choose “Network and Sharing Center.” Connect your PC to a Wi-Fi network.
- Under “Change your networking settings,” click on “Troubleshoot problems.”
- The PC troubleshooter will now scan for any potential issues with your network connection. Please select the type of network connection you are using: wired or wireless.
- Once complete, the network adapter will provide recommendations or prompt you to select and connect your PC to resolve any identified problems.
By following these steps, you can leverage the power of your pc’s built-in Network Troubleshooter to quickly identify and fix common network connectivity issues. Select the type of issue you’re experiencing and let Windows’ Network Troubleshooter do the rest.
Understanding the information provided by diagnostic tools
Diagnostic tools like ipconfig not only connect and provide information about your current network configuration but also offer insights into potential issues. By using this type of tool, you can easily select the network you want to troubleshoot and gather the necessary data for analysis. For example, if you notice that your PC’s network adapter cannot connect to a Wi-Fi network and your IP address starts with “169.254,” it indicates a problem with obtaining an IP address from the DHCP server. This information can help you narrow down the root cause of your connectivity problem with your network adapter. Select the appropriate network adapter on your PC to troubleshoot the issue with your Wi-Fi network.
Similarly, tools like pathping and netsh winsock reset can be used to diagnose more complex network issues on a PC. These tools can help users connect to Wi-Fi and select the appropriate network. Pathping combines the functionality of ping and tracert, allowing you to connect your PC to a network and select the path to track packet loss and latency along the network path. On the other hand, if you are experiencing issues with your PC’s network protocols, you can use the netsh winsock reset command to connect to a Wi-Fi network and select the default state for the Windows Sockets API.
Advanced Network Commands for Diagnostics
Having access to advanced network commands can be incredibly helpful when you need to connect, select, or troubleshoot your Wi-Fi connection. These command-line tools, such as fi and select, allow you to gather detailed information about your network settings and diagnose any problems that may be affecting your connection.
One of the most commonly used commands is ipconfig, which displays the IP configuration for all available networks on your computer. This command helps you connect and select the appropriate network. By typing ipconfig in the command prompt and pressing enter, you can view important details such as your IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and network adapter. This information can help you select and connect to a Wi-Fi network, and identify if there are any issues with your network settings.
Examples of useful commands such as ipconfig, ping, and tracert
Another powerful command is ping. This command allows you to test the connectivity between your computer and another device or website by sending a small packet of data using the network adapter and measuring the response time over a Wi-Fi network. To perform this test, select the appropriate network adapter and initiate the command. By typing ping followed by the IP address or domain name of the device or website you want to test, you can check if there is a successful connection using your network adapter. If there are any delays or timeouts in the response, it could indicate a problem with your network connection. In the event of fi or select delays or timeouts in the response, it could indicate a problem with your network connection.
Similarly, the tracert command is another valuable tool that helps trace the route packets take from your computer to a destination on a network. This can be especially useful when troubleshooting connectivity issues with your network adapter. By using tracert, you can identify any potential bottlenecks or connectivity problems along the way, ensuring a smooth connection between your computer and the desired destination. By typing tracert followed by an IP address or domain name, you can see each hop along the path and measure how long it takes for packets to reach each one using a network adapter. This can help pinpoint where exactly in the network there might be an issue causing slow or interrupted connections. By using the “fi” command, you can select the specific area of the network to analyze for potential issues.
How to interpret the output of these commands to identify network issues
Interpreting the output of these networking commands requires some understanding of how to connect and select Wi-Fi networks. For example, if you run ping and receive responses with high latency or timeouts consistently, it could suggest a problem with your internet connection or the device you are trying to reach. This could be due to issues with your network adapter or Wi-Fi connection. Make sure to select the appropriate network adapter and check your Wi-Fi settings.
When using tracert, if you notice delays or timeouts at a specific hop, it could indicate an issue with a particular network node. This could affect your ability to connect and select the desired network. You can use this information to report the problem to your network administrator or internet service provider for further investigation. If you are unable to connect to the internet, make sure you select the correct Wi-Fi network and check if your Wi-Fi is on.
In addition to these commands, there are other advanced troubleshooting techniques available for network adapters. For instance, the network adapter can help you connect and select DNS servers for specific domain names and IP addresses.
By familiarizing yourself with these command-line tools, such as ‘fi’ and ‘select’, and understanding how to interpret their output, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve network connectivity issues on your Windows computer.
Addressing Wi-Fi Connection Challenges
Common Wi-Fi connection problems and their causes
Wi-Fi connection issues, such as problems with the network adapter, can be frustrating. However, understanding these common issues and their causes can help you select the right troubleshooting steps to resolve them effectively. One of the most frequent issues is a weak or unstable wireless signal when trying to connect using a network adapter. This can occur due to physical barriers like walls or distance from the router, as well as interference from other devices or neighboring networks. In such cases, it may be difficult to connect or select the desired network.
Another common problem is incorrect wireless mode settings on your router, which can affect the network adapter’s ability to connect. Make sure to select the proper mode to ensure a successful connection. If your device and router are not using compatible modes, it can lead to connectivity problems. It is important to select the appropriate mode for both your device and router. Outdated firmware on your router or network adapter can also cause issues with your Wi-Fi connection. It is important to select and update the firmware regularly to avoid these problems.
Tips for improving Wi-Fi signal strength and range
To enhance your Wi-Fi signal strength and range, you can connect and select a few simple steps. First, try repositioning your wireless router to a central location in your home or office to connect and select the best signal. This will help ensure that the signal can connect and reach all areas more evenly. By selecting the appropriate settings, you can optimize the signal strength throughout your space.
You should also avoid placing the router near other electronic devices that may interfere with the signal, such as cordless phones or microwave ovens. Connecting and selecting the router near other electronic devices that may interfere with the signal, such as cordless phones or microwave ovens is not recommended. These select appliances operate on similar frequencies to Wi-Fi signals and can disrupt the connection.
If you’re still experiencing weak signal strength, consider using a Wi-Fi range extender or repeater to connect and select a stronger signal. These devices select and amplify the existing signal and extend its coverage area, allowing you to connect to Wi-Fi in areas that were previously out of reach.
Troubleshooting steps specific to wireless networks
When troubleshooting wireless network connectivity issues, you can follow several steps to select the right solution.
- Sometimes, to resolve temporary glitches that may be affecting your connection, you can select to restart your router.
- Check for firmware updates: Ensure that both your router and network adapter have the latest firmware installed to connect and select. Manufacturers often release updates to connect with users, address known issues, and select improvements for better performance.
- Verify IP addresses: Select and confirm that both your computer’s IP address and default gateway match the settings recommended by your internet service provider (ISP). Incorrect IP configurations can prevent proper communication with the router. It is important to select the correct IP settings for seamless communication.
- Temporarily select disabling wireless security: Temporarily disabling select security measures like WPA or WEP encryption can help determine if they are causing connection problems. If the issue resolves when security is turned off, you may need to select and adjust your security settings or consider using a different encryption method.
- Select to connect directly to the router: By selecting to connect your computer directly to the router using an Ethernet cable, you can determine if the issue lies with your Wi-Fi network or another factor.
Remember, troubleshooting steps may vary depending on the specific setup and equipment you select. It’s always a good idea to select and consult manufacturer documentation or online resources for detailed instructions tailored to your situation.
Resolving Network Adapter and Driver Issues
Identifying potential problems with network adapters and drivers
One of the key areas to focus on is to select the network adapter and its associated driver. A network adapter, also known as a network interface card (NIC), is responsible for connecting your computer to a select local area network (LAN) or a wireless network.
If you are experiencing problems with your network connection, it is essential to select and identify any potential issues with your network adapter and driver. Start by checking if the adapter you select is properly installed and recognized by your computer. You can select to do this by accessing the Device Manager, which provides an overview of all hardware devices connected to your system.
Updating or reinstalling network drivers for improved performance
Outdated or incompatible drivers can often cause connectivity problems. To ensure optimal performance, it is crucial to regularly select and update your network adapter drivers. The first step is to select and identify the make and model of your network adapter. Once you have this information, select the manufacturer’s website or use Windows Update to find and install the latest driver software.
In select cases, updating the driver may not entirely resolve the issue. If you continue experiencing connectivity problems after updating the driver, select to consider uninstalling and reinstalling it. This process can help select and eliminate any corrupted files or settings that might be causing conflicts.
Troubleshooting steps for resolving adapter-related issues
If you are still encountering difficulties with your network connection after updating or reinstalling the driver, there are additional troubleshooting steps you can select to take.
- Run the Network Adapter Troubleshooter: Windows includes a built-in troubleshooter specifically designed to diagnose and fix common networking problems related to select adapters. Using this tool, you can select and automatically detect and resolve many issues.
- Check for physical damage: Select inspect both ends of Ethernet cables for any signs of damage or loose connections. Similarly, if you want to select a wireless adapter, ensure that it is securely inserted into the appropriate port.
- Temporarily select disabling and re-enabling the network adapter can sometimes resolve connectivity issues. This action allows you to select and reset the adapter’s settings, which can help establish a fresh connection.
- Restart your computer: Select a simple restart can often resolve temporary glitches or conflicts that may be affecting your network connection.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively select and address network adapter and driver issues that may be causing connectivity problems on your Windows device. Remember to always select and keep your drivers up to date to ensure optimal performance.
Additional Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Exploring advanced techniques for diagnosing complex network problems
Sometimes the basic troubleshooting steps may not be sufficient. In such cases, it is essential to select delve into more advanced techniques to diagnose and resolve complex problems. By utilizing these additional troubleshooting steps, you can select the right approach to gain deeper insights into the root causes of network issues and effectively resolve them.
One technique for troubleshooting connectivity issues involves analyzing event logs and error messages to select clues. Event logs are a vital tool to select and gather valuable information about system events, errors, and warnings. These logs can help identify and troubleshoot network-related problems. By examining these logs, you can select and pinpoint specific errors or patterns that might be causing connectivity issues. For example, if you notice frequent DNS errors in the event logs, it could indicate a problem with your DNS server configuration.
Utilizing third-party software tools for in-depth network analysis
In addition to event logs and error messages, there are various third-party software tools available that can assist in conducting in-depth network analysis. These tools allow users to select the most suitable options for their analysis needs. These select tools offer advanced features and functionalities designed specifically for troubleshooting complex network problems.
For instance, select tools allow you to perform packet captures and analyze network traffic at a granular level. This enables you to select and identify any anomalies or bottlenecks that could be affecting your network connectivity. By examining the round trip times (RTTs) of packets sent between devices on your network, you can select and determine if there are any latency issues or packet loss occurring.
Another useful feature provided by certain software tools is the ability to select and monitor wireless networks. With this capability, you can select and assess signal strength, channel congestion, and interference levels within your Wi-Fi environment. By identifying potential sources of interference or weak signal areas, you can select appropriate measures such as adjusting router settings or relocating devices to improve overall network performance.
Moreover, select tools offer diagnostic utilities that can automatically detect common networking issues and suggest fixes accordingly. These select utilities often cover a wide range of problems, including select issues with network adapters, TCP/IP configurations, and firewall settings. By leveraging these select diagnostic utilities, you can save time and effort in manually troubleshooting each potential problem.
Data Collection and Testing for Connectivity Issues
Importance of collecting data and performing tests during troubleshooting process
One of the most crucial steps in the data analysis process is to select and collect relevant data, and then perform tests to analyze it. This helps in selecting and identifying the root cause of the problem and finding a select appropriate solution. Without proper data collection and testing, it can be challenging to select and pinpoint the exact issue, leading to prolonged downtime and frustration.
By gathering relevant network information, such as connection state machine details, signal strength, cable modem data, and frequency band selection, you can gain valuable insights into the health of your network. This information acts as a starting point for further investigation and analysis. It is important to select the right data for analysis.
Recommended tools and methods for gathering relevant network information
To collect accurate data about your network connectivity issues, there are several recommended tools and methods you can utilize. One commonly used tool is the ping test. By using the Command Prompt or PowerShell, you can send ICMP echo requests to a specific IP address or domain name to check if there’s a response. The ping statistics will provide valuable information about packet loss, latency, and overall network performance.
Another useful method is checking physical connections. Ensure that all cables are securely connected to their respective ports on devices such as routers, switches, or modems. A loose or faulty cable could be causing intermittent connection issues.
You can use built-in Windows utilities like Network Diagnostics (found in Network & Internet settings) or troubleshooters specific to certain types of connections (e.g., Wi-Fi troubleshooter). These tools automatically scan your system for potential problems and provide suggestions for resolving them.
Conducting thorough tests to pinpoint the root cause of connectivity problems
Once you have collected initial data about your network connectivity issues, it’s time to conduct thorough tests to narrow down the root cause. Start by isolating individual components of your network setup—such as routers, switches, or access points—and test each one separately.
For example, if you’re experiencing Wi-Fi connection issues, try connecting to different Wi-Fi networks or using a different device to see if the problem persists. This helps determine whether the issue lies with your specific network or the device you’re using.
You can also perform TCP/IP stack resets, which reset various network configurations and settings back to their default values. This can resolve issues related to IP address conflicts or corrupted network configurations.
If all else fails, consider reaching out to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for assistance. They may be able to identify any network infrastructure problems on their end or provide guidance on resolving the connectivity issue.
Maintenance and Preventive Measures for Network Stability
Best Practices for Maintaining a Stable Network Connection in Windows
To ensure a stable network connection in Windows, it is essential to follow some best practices. Firstly, regularly updating the firmware and software for network devices is crucial. Manufacturers frequently release updates to improve performance, fix bugs, and address security vulnerabilities. By keeping your devices up to date, you can enhance network stability and prevent potential issues.
Another important practice is to monitor and manage your network profile effectively. Windows allows you to categorize your network as either public or private, with different security settings applied accordingly. It is recommended to set the appropriate profile based on the nature of your network usage. For example, if you are connected to a public Wi-Fi hotspot, selecting the public profile will enable additional security measures.
Optimizing power settings can contribute to maintaining a stable network connection. Power-saving features may sometimes interfere with network performance by limiting the power allocated to networking components. By adjusting power settings appropriately or disabling certain power-saving options, you can ensure consistent connectivity.
Regularly Updating Firmware and Software for Network Devices
Updating firmware and software for your network devices should be performed regularly as part of routine maintenance. Firmware refers to the embedded software that controls the functionality of hardware components within a device such as routers or switches. Software updates often include bug fixes, feature enhancements, and compatibility improvements.
By applying these updates promptly when they become available from manufacturers’ websites or through automatic update mechanisms provided by the devices themselves (if applicable), you can minimize potential vulnerabilities that could compromise your network’s stability.
Implementing Security Measures to Protect Against Network Vulnerabilities
Network vulnerabilities pose significant risks to both individual users and organizations alike. It is crucial to implement robust security measures that protect against these threats. One effective measure is enabling encryption protocols such as WPA2 or WPA3 on your wireless networks. These protocols encrypt data transmitted over the network, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to intercept and exploit sensitive information.
Another important security measure is using strong and unique passwords for your network devices. Weak or easily guessable passwords can make your network susceptible to brute-force attacks. By creating complex passwords that include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, you can significantly enhance the security of your network.
Furthermore, regularly updating antivirus software on all devices connected to your network is essential. Antivirus software helps detect and remove malware that could potentially compromise your network’s stability. Enabling firewalls on both individual devices and routers adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access attempts.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve now become an advanced troubleshooter for Windows network connectivity issues. Armed with the knowledge and techniques outlined in this article, you’re well-equipped to tackle even the most stubborn network problems. Remember, troubleshooting is a process of elimination, so be patient and methodical in your approach. Don’t hesitate to use the various tools and commands at your disposal, and always keep an eye out for potential Wi-Fi and adapter-related challenges.
In today’s interconnected world, a stable and reliable network connection is crucial. By mastering these advanced troubleshooting techniques, you can ensure that your network stays up and running smoothly, enabling you to work, connect, and enjoy online experiences without interruption. So go ahead, put your newfound skills into practice, and don’t be afraid to explore further resources to deepen your understanding. Happy troubleshooting!
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
How can I troubleshoot network connectivity issues on Windows?
To troubleshoot network connectivity issues on Windows, you can start by using the built-in Windows Network Diagnostics tools. These tools can automatically detect and fix common network problems. If the issue persists, you can try advanced troubleshooting techniques such as using network commands and addressing Wi-Fi connection challenges.
What are some initial steps to take when facing network problems on Windows?
When facing network problems on Windows, you should first check if your internet service provider is experiencing any outages. Then, ensure that your modem and router are properly connected and functioning. Restarting your devices and checking for any software updates can also help resolve common network issues.
How do I use Windows Network Diagnostics tools to diagnose network problems?
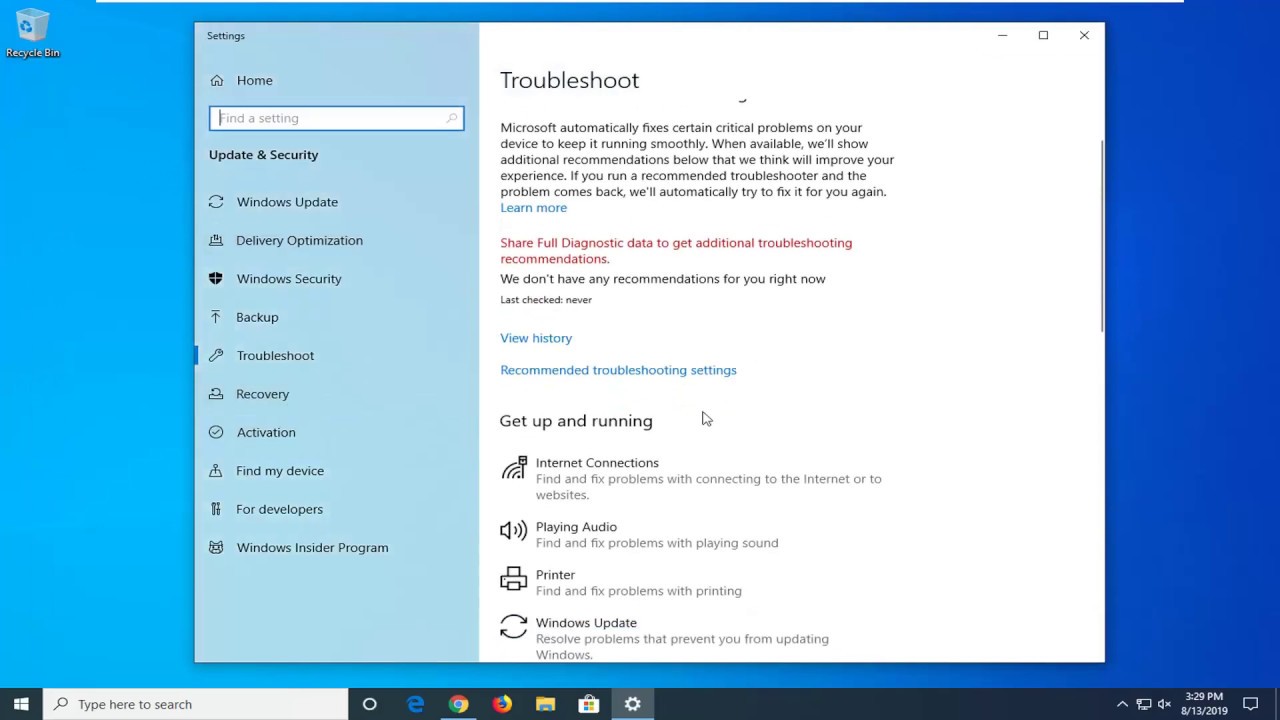
To use the Windows Network Diagnostics tools, go to the “Network & Internet” settings in your Control Panel or Settings app. From there, select “Troubleshoot” and choose the appropriate option based on the specific network problem you’re experiencing. The diagnostics tool will then attempt to identify and fix the issue.
What are some advanced network commands I can use for diagnostics?
Some advanced network commands for diagnostics include ipconfig (to view IP configuration), ping (to test connectivity with another device), tracert (to trace the route taken by packets), and netstat (to display active connections). These commands provide detailed information about your network connection and help identify potential issues.
How can I address Wi-Fi connection challenges on Windows?
To address Wi-Fi connection challenges on Windows, you can try simple steps like restarting your computer or resetting your wireless router. You may also need to update your Wi-Fi adapter drivers or adjust the wireless channel settings to reduce interference from other devices. Ensuring that you’re within range of the Wi-Fi signal can improve connectivity.